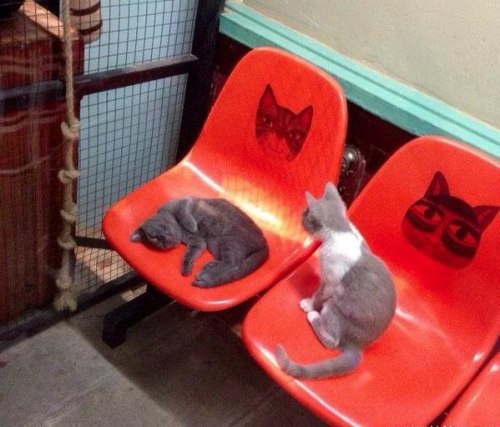
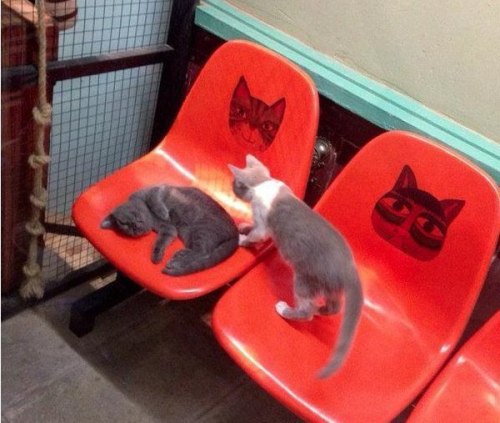
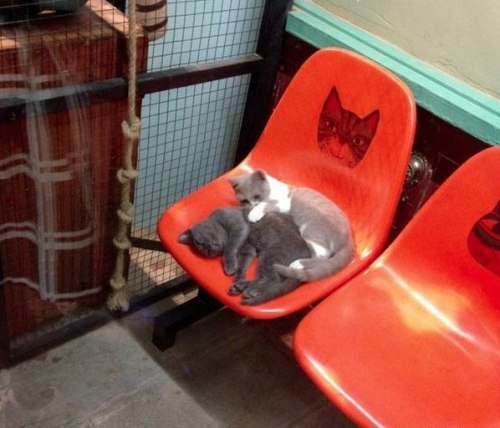
139 posts
Latest Posts by artemis-ncc1701d - Page 2









February starts for Uhura challenge. List by @timelordofmanynames

Rest in peace to Hollywood legend Kirk Douglas, remembered by sci fi fans for his role as Adam in “Saturn 3″ (1980) but much better known for a long and distinguished acting career in more mainstream films including Stanley Kubrick’s 1960 epic “Spartacus”.
The actor, producer, director, philanthropist and author died yesterday on 5 February 2020 at the age of 103.
What would happen if I go into a black hole? Do you think I would disappear forever or would I still exist inside the black hole?
I call this one “Pemberley” 🏰 More to come! #Bloodlust&Bonnets #graphicnovel https://www.instagram.com/p/B1bnV4SHa5x/?igshid=gg2l9vn1yc26
Sooon!

Sweet 😚


Astronauts talking about viewing the earth from the moon, from The Overview Effect: Awe and Self-Transcendent Experience in Space Flight

Say hello to the Butterfly Nebula 👋
It looks like our Hubble Space Telescope captured an image of a peaceful, cosmic butterfly unfurling its celestial wings, but the truth is vastly more violent. In the Butterfly Nebula, layers of gas are being ejected from a dying star. Medium-mass stars grow unstable as they run out of fuel, which leads them to blast tons of material out into space at speeds of over a million miles per hour!
Streams of intense ultraviolet radiation cause the cast-off material to glow, but eventually the nebula will fade and leave behind only a small stellar corpse called a white dwarf. Our middle-aged Sun can expect a similar fate once it runs out of fuel in about six billion years.
Planetary nebulas like this one aren’t actually related to planets; the term was coined by astronomer William Herschel, who actually discovered the Butterfly Nebula in 1826. Through his small telescope, planetary nebulas looked like glowing, planet-like orbs. While stars that generate planetary nebulas may have once had planets orbiting them, scientists expect that the fiery death throes these stars undergo will ultimately leave any planets in their vicinity completely uninhabitable.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
I was thinking about the difference between how Spock has been treated all his life ( TOS Spock) by others including his mother and then there’s Jim.
In the following scene, Amanda tries to elicit emotions out of Spock.

The thing is, Spock doesn’t need to be reminded that he has a human part. Every single moment of his childhood he struggles with it. By this age, in this scene above, he has displayed incredible personal courage to handle it. He has dived deep to realize who is he is. Neither human nor Vulcan but choosing to be more Vulcan because he is drawn to those values.
She then goes on to remind him why he was in anguish.

Yes, the other boys tormented him. The point is he understands that. He is a grown man now. He is extremely intelligent and is respected throughout the quadrant. She though shows no respect for him. She tries to revert him back to the helpless and struggling five year old he was. Because that for her is when she can connect with him. Even as a five year old he had stopped opening up to her. Because - while the other boys tormented him, they were still strangers. It was still possible to process non-acceptance from others. But own mother?
The she does this.

So, after the “other boys” had tormented him. what does she think she has done just now? Has been doing?
Contrast that with following scene.

Notice Jim, having known Spock for a long time, still doesn’t assume anything. He asks. He asks if Spock feels insulted. They both know the previous scene was insulting. This is the critical difference. He shows respect for Spock. Gives Spock an opportunity to express his emotions as Spock wants to - not how he is supposed to. Something Amanda never does. Or Sarek. Spock responds in his own unique way. He doesn’t say “No, Jim, I am fine”. He conveys how he does feel insulted but he is also wise enough to realize how emotions work. That simply acknowleding emtoions is child’s play. To be wiser beyond that, one has to understand that emotions come and go. And that it’s in our control. We can choose to let go of an emotion and no longer feel insulted. This is what Spock has been striving for. This is something he tried to tell Amanda when he says “how can you live on Vulcan and not understand Vulcan”.
So, Jim, who is NOT Vulcan, nor tries to be, and is a very emotional man, how does he respond to this moment?

Good. Why, good? Because Jim is saying, “I am glad you’re in touch with your values. It’s good because I want you to be exactly who you are.”
Jim doesn’t lecture Spock about his human side nor does he insult Spock by mocking his Vulcan ethics, which are in constrast to all the humans onboard the ship. He accepst Spock and supports Spock for what Spock has chosen to be. And he does what Spock’s parents or family never did.
“We’ll tackle him together.” He says “WE”. The unspoken message is - You and me, we are equal, I “see” you. I feel seen by you. (You have put up with my kind of insanity). I respect you. I respect your struggles and admire what you have become and continue to become. With you by my side, I feel stronger. You don’t have to rescue me. I don’t have to rescue you. We can tackle this TOGETHER.”
And this is why Jim and Spock are what they are to each other.


#InternationalCatDay? Try #IntergalacticCatDay.
Check out features of our feline friends that have come to life as interstellar phenomena!
Pictured first, the Cat’s Paw Nebula is located about 4,200-5,500 light-years from Earth – situated in our very own Milky Way Galaxy. It was named for the large, round features that create the impression of a feline footprint and was captured by our Spitzer Space Telescope. After gas and dust inside the nebula collapse to form stars, the stars may in turn heat up the pressurized gas surrounding them. This process causes the gas to expand into space and form the bright red bubbles you see. The green areas show places where radiation from hot stars collided with large molecules called “polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons,” causing them to fluoresce.
Next, you’ll find the Cat’s Eye Nebula. Residing 3,000 light-years from Earth, the Cat’s Eye represents a brief, yet glorious, phase in the life of a sun-like star. This nebula’s dying central star may have produced the simple, outer pattern of dusty concentric shells by shrugging off outer layers in a series of regular convulsions. To create this view, Hubble Space Telescope archival image data have been reprocessed. Compared to well-known Hubble pictures, the alternative processing strives to sharpen and improve the visibility of details in light and dark areas of the nebula and also applies a more complex color palette. Gazing into the Cat’s Eye, astronomers may well be seeing the fate of our sun, destined to enter its own planetary nebula phase of evolution … in about 5 billion years.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Black Holes are NICER Than You Think!
We’re learning more every day about black holes thanks to one of the instruments aboard the International Space Station! Our Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) instrument is keeping an eye on some of the most mysterious cosmic phenomena.

We’re going to talk about some of the amazing new things NICER is showing us about black holes. But first, let’s talk about black holes — how do they work, and where do they come from? There are two important types of black holes we’ll talk about here: stellar and supermassive. Stellar mass black holes are three to dozens of times as massive as our Sun while supermassive black holes can be billions of times as massive!

Stellar black holes begin with a bang — literally! They are one of the possible objects left over after a large star dies in a supernova explosion. Scientists think there are as many as a billion stellar mass black holes in our Milky Way galaxy alone!
Supermassive black holes have remained rather mysterious in comparison. Data suggest that supermassive black holes could be created when multiple black holes merge and make a bigger one. Or that these black holes formed during the early stages of galaxy formation, born when massive clouds of gas collapsed billions of years ago. There is very strong evidence that a supermassive black hole lies at the center of all large galaxies, as in our Milky Way.

Imagine an object 10 times more massive than the Sun squeezed into a sphere approximately the diameter of New York City — or cramming a billion trillion people into a car! These two examples give a sense of how incredibly compact and dense black holes can be.
Because so much stuff is squished into such a relatively small volume, a black hole’s gravity is strong enough that nothing — not even light — can escape from it. But if light can’t escape a dark fate when it encounters a black hole, how can we “see” black holes?

Scientists can’t observe black holes directly, because light can’t escape to bring us information about what’s going on inside them. Instead, they detect the presence of black holes indirectly — by looking for their effects on the cosmic objects around them. We see stars orbiting something massive but invisible to our telescopes, or even disappearing entirely!
When a star approaches a black hole’s event horizon — the point of no return — it’s torn apart. A technical term for this is “spaghettification” — we’re not kidding! Cosmic objects that go through the process of spaghettification become vertically stretched and horizontally compressed into thin, long shapes like noodles.

Scientists can also look for accretion disks when searching for black holes. These disks are relatively flat sheets of gas and dust that surround a cosmic object such as a star or black hole. The material in the disk swirls around and around, until it falls into the black hole. And because of the friction created by the constant movement, the material becomes super hot and emits light, including X-rays.
At last — light! Different wavelengths of light coming from accretion disks are something we can see with our instruments. This reveals important information about black holes, even though we can’t see them directly.

So what has NICER helped us learn about black holes? One of the objects this instrument has studied during its time aboard the International Space Station is the ever-so-forgettably-named black hole GRS 1915+105, which lies nearly 36,000 light-years — or 200 million billion miles — away, in the direction of the constellation Aquila.
Scientists have found disk winds — fast streams of gas created by heat or pressure — near this black hole. Disk winds are pretty peculiar, and we still have a lot of questions about them. Where do they come from? And do they change the shape of the accretion disk?

It’s been difficult to answer these questions, but NICER is more sensitive than previous missions designed to return similar science data. Plus NICER often looks at GRS 1915+105 so it can see changes over time.
NICER’s observations of GRS 1915+105 have provided astronomers a prime example of disk wind patterns, allowing scientists to construct models that can help us better understand how accretion disks and their outflows around black holes work.

NICER has also collected data on a stellar mass black hole with another long name — MAXI J1535-571 (we can call it J1535 for short) — adding to information provided by NuSTAR, Chandra, and MAXI. Even though these are all X-ray detectors, their observations tell us something slightly different about J1535, complementing each other’s data!
This rapidly spinning black hole is part of a binary system, slurping material off its partner, a star. A thin halo of hot gas above the disk illuminates the accretion disk and causes it to glow in X-ray light, which reveals still more information about the shape, temperature, and even the chemical content of the disk. And it turns out that J1535’s disk may be warped!

Image courtesy of NRAO/AUI and Artist: John Kagaya (Hoshi No Techou)
This isn’t the first time we have seen evidence for a warped disk, but J1535’s disk can help us learn more about stellar black holes in binary systems, such as how they feed off their companions and how the accretion disks around black holes are structured.
NICER primarily studies neutron stars — it’s in the name! These are lighter-weight relatives of black holes that can be formed when stars explode. But NICER is also changing what we know about many types of X-ray sources. Thanks to NICER’s efforts, we are one step closer to a complete picture of black holes. And hey, that’s pretty nice!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Solar System 10 Things: Two Years of Juno at Jupiter
Our Juno mission arrived at the King of Planets in July 2016. The intrepid robotic explorer has been revealing Jupiter’s secrets ever since.
Here are 10 historic Juno mission highlights:

1. Arrival at a Colossus
After an odyssey of almost five years and 1.7 billion miles (2.7 billion kilometers), our Juno spacecraft fired its main engine to enter orbit around Jupiter on July 4, 2016. Juno, with its suite of nine science instruments, was the first spacecraft to orbit the giant planet since the Galileo mission in the 1990s. It would be the first mission to make repeated excursions close to the cloud tops, deep inside the planet’s powerful radiation belts.

2. Science, Meet Art
Juno carries a color camera called JunoCam. In a remarkable first for a deep space mission, the Juno team reached out to the general public not only to help plan which pictures JunoCam would take, but also to process and enhance the resulting visual data. The results include some of the most beautiful images in the history of space exploration.

3. A Whole New Jupiter
It didn’t take long for Juno—and the science teams who hungrily consumed the data it sent home—to turn theories about how Jupiter works inside out. Among the early findings: Jupiter’s poles are covered in Earth-sized swirling storms that are densely clustered and rubbing together. Jupiter’s iconic belts and zones were surprising, with the belt near the equator penetrating far beneath the clouds, and the belts and zones at other latitudes seeming to evolve to other structures below the surface.
4. The Ultimate Classroom
The Goldstone Apple Valley Radio Telescope (GAVRT) project, a collaboration among NASA, JPL and the Lewis Center for Educational Research, lets students do real science with a large radio telescope. GAVRT data includes Jupiter observations relevant to Juno, and Juno scientists collaborate with the students and their teachers.
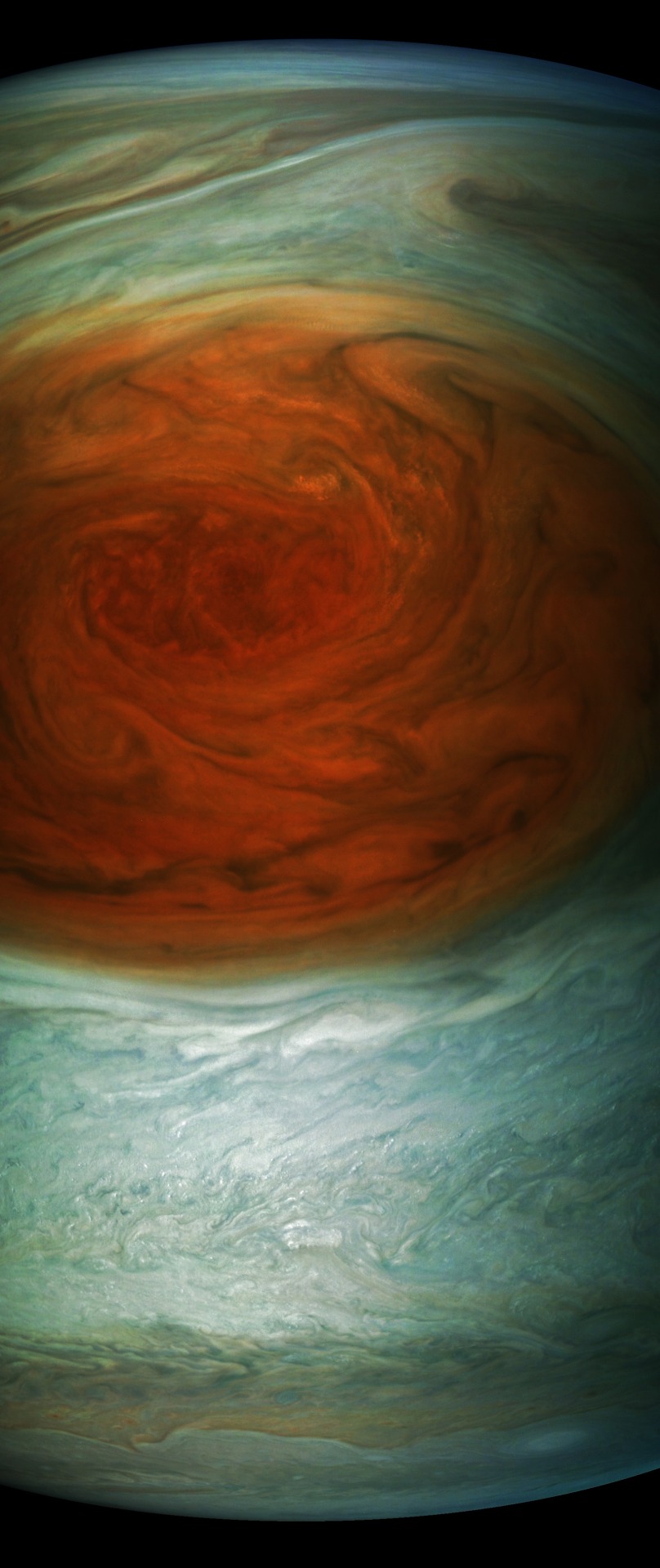

5. Spotting the Spot
Measuring in at 10,159 miles (16,350 kilometers) in width (as of April 3, 2017) Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is 1.3 times as wide as Earth. The storm has been monitored since 1830 and has possibly existed for more than 350 years. In modern times, the Great Red Spot has appeared to be shrinking. In July 2017, Juno passed directly over the spot, and JunoCam images revealed a tangle of dark, veinous clouds weaving their way through a massive crimson oval.
“For hundreds of years scientists have been observing, wondering and theorizing about Jupiter’s Great Red Spot,” said Scott Bolton, Juno principal investigator from the Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio. “Now we have the best pictures ever of this iconic storm. It will take us some time to analyze all the data from not only JunoCam, but Juno’s eight science instruments, to shed some new light on the past, present and future of the Great Red Spot.”

6. Beauty Runs Deep
Data collected by the Juno spacecraft during its first pass over Jupiter’s Great Red Spot in July 2017 indicate that this iconic feature penetrates well below the clouds. The solar system’s most famous storm appears to have roots that penetrate about 200 miles (300 kilometers) into the planet’s atmosphere.

7. Powerful Auroras, Powerful Mysteries
Scientists on the Juno mission observed massive amounts of energy swirling over Jupiter’s polar regions that contribute to the giant planet’s powerful auroras – only not in ways the researchers expected. Examining data collected by the ultraviolet spectrograph and energetic-particle detector instruments aboard Juno, scientists observed signatures of powerful electric potentials, aligned with Jupiter’s magnetic field, that accelerate electrons toward the Jovian atmosphere at energies up to 400,000 electron volts. This is 10 to 30 times higher than the largest such auroral potentials observed at Earth.
Jupiter has the most powerful auroras in the solar system, so the team was not surprised that electric potentials play a role in their generation. What puzzled the researchers is that despite the magnitudes of these potentials at Jupiter, they are observed only sometimes and are not the source of the most intense auroras, as they are at Earth.
8. Heat from Within
Juno scientists shared a 3D infrared movie depicting densely packed cyclones and anticyclones that permeate the planet’s polar regions, and the first detailed view of a dynamo, or engine, powering the magnetic field for any planet beyond Earth (video above). Juno mission scientists took data collected by the spacecraft’s Jovian InfraRed Auroral Mapper (JIRAM) instrument and generated a 3D fly-around of the Jovian world’s north pole.
Imaging in the infrared part of the spectrum, JIRAM captures light emerging from deep inside Jupiter equally well, night or day. The instrument probes the weather layer down to 30 to 45 miles (50 to 70 kilometers) below Jupiter’s cloud tops.

9. A Highly Charged Atmosphere
Powerful bolts of lightning light up Jupiter’s clouds. In some ways its lightning is just like what we’re used to on Earth. In other ways,it’s very different. For example, most of Earth’s lightning strikes near the equator; on Jupiter, it’s mostly around the poles.

10. Extra Innings
In June, we approved an update to Juno’s science operations until July 2021. This provides for an additional 41 months in orbit around. Juno is in 53-day orbits rather than 14-day orbits as initially planned because of a concern about valves on the spacecraft’s fuel system. This longer orbit means that it will take more time to collect the needed science data, but an independent panel of experts confirmed that Juno is on track to achieve its science objectives and is already returning spectacular results. The spacecraft and all its instruments are healthy and operating nominally.
Read the full web version of this week’s ‘Solar System: 10 Things to Know’ article HERE.
For regular updates, follow NASA Solar System on Twitter and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
I hope I have a wedding like this some day!



Our friends had a magical woodland wedding and invited the faeries along! We were very well behaved and were rewarded with some lovely memories and these fantastic photos by Jennifer Alyse Rogers Photography. 💖✨💖✨💖
10 Things: Mars Helicopter
When our next Mars rover lands on the Red Planet in 2021, it will deliver a groundbreaking technology demonstration: the first helicopter to ever fly on a planetary body other than Earth. This Mars Helicopter will demonstrate the first controlled, powered, sustained flight on another world. It could also pave the way for future missions that guide rovers and gather science data and images at locations previously inaccessible on Mars. This exciting new technology could change the way we explore Mars.

1. Its body is small, but its blades are mighty.
One of the biggest engineering challenges is getting the Mars Helicopter’s blades just right. They need to push enough air downward to receive an upward force that allows for thrust and controlled flight — a big concern on a planet where the atmosphere is only one percent as dense as Earth’s. “No helicopter has flown in those flight conditions – equivalent to 100,000 feet (30,000 meters) on Earth,” said Bob Balaram, chief engineer for the project at our Jet Propulsion Laboratory.

2. It has to fly in really thin Martian air.
To compensate for Mars’ thin atmosphere, the blades must spin much faster than on an Earth helicopter, and the blade size relative to the weight of the helicopter has to be larger too. The Mars Helicopter’s rotors measure 4 feet wide (about 1.2 meters) long, tip to tip. At 2,800 rotations per minute, it will spin about 10 times faster than an Earth helicopter. At the same time, the blades shouldn’t flap around too much, as the helicopter’s design team discovered during testing. Their solution: make the blades more rigid. “Our blades are much stiffer than any terrestrial helicopter’s would need to be,” Balaram said. The body, meanwhile, is tiny — about the size of a softball. In total, the helicopter will weigh just under 4 pounds (1.8 kilograms).

3. It will make up to five flights on Mars.
Over a 30-day period on Mars, the helicopter will attempt up to five flights, each time going farther than the last. The helicopter will fly up to 90 seconds at a time, at heights of up to 10 to 15 feet (3 to 5 meters). Engineers will learn a lot about flying a helicopter on Mars with each flight, since it’s never been done before!

4. The Mars Helicopter team has already completed groundbreaking tests.
Because a helicopter has never visited Mars before, the Mars Helicopter team has worked hard to figure out how to predict the helicopter’s performance on the Red Planet. “We had to invent how to do planetary helicopter testing on Earth,” said Joe Melko, deputy chief engineer of Mars Helicopter, based at JPL.
The team, led by JPL and including members from JPL, AeroVironment Inc., Ames Research Center, and Langley Research Center, has designed, built and tested a series of test vehicles.
In 2016, the team flew a full-scale prototype test model of the helicopter in the 25-foot (7.6-meter) space simulator at JPL. The chamber simulated the low pressure of the Martian atmosphere. More recently, in 2018, the team built a fully autonomous helicopter designed to operate on Mars, and successfully flew it in the 25-foot chamber in Mars-like atmospheric density.
Engineers have also exercised the rotors of a test helicopter in a cold chamber to simulate the low temperatures of Mars at night. In addition, they have taken design steps to deal with Mars-like radiation conditions. They have also tested the helicopter’s landing gear on Mars-like terrain. More tests are coming to see how it performs with Mars-like winds and other conditions.

5. The camera is as good as your cell phone camera.
The helicopter’s first priority is successfully flying on Mars, so engineering information takes priority. An added bonus is its camera. The Mars Helicopter has the ability to take color photos with a 13-megapixel camera — the same type commonly found in smart phones today. Engineers will attempt to take plenty of good pictures.
6. It’s battery-powered, but the battery is rechargeable.
The helicopter requires 360 watts of power for each second it hovers in the Martian atmosphere – equivalent to the power required by six regular lightbulbs. But it isn’t out of luck when its lithium-ion batteries run dry. A solar array on the helicopter will recharge the batteries, making it a self-sufficient system as long as there is adequate sunlight. Most of the energy will be used to keep the helicopter warm, since nighttime temperatures on Mars plummet to around minus 130 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 90 Celsius). During daytime flights, temperatures may rise to a much warmer minus 13 to minus 58 degrees Fahrenheit to (minus 25 to minus 50 degrees Celsius) — still chilly by Earth standards. The solar panel makes an average of 3 watts of power continuously during a 12-hour Martian day.
7. The helicopter will be carried to Mars under the belly of the rover.
Somewhere between 60 to 90 Martian days (or sols) after the Mars 2020 rover lands, the helicopter will be deployed from the underside of the rover. Mars Helicopter Delivery System on the rover will rotate the helicopter down from the rover and release it onto the ground. The rover will then drive away to a safe distance.

8. The helicopter will talk to the rover.
The Mars 2020 rover will act as a telecommunication relay, receiving commands from engineers back on Earth and relaying them to the helicopter. The helicopter will then send images and information about its own performance to the rover, which will send them back to Earth. The rover will also take measurements of wind and atmospheric data to help flight controllers on Earth.
9. It has to fly by itself, with some help.
Radio signals take time to travel to Mars — between four and 21 minutes, depending on where Earth and Mars are in their orbits — so instantaneous communication with the helicopter will be impossible. That means flight controllers can’t use a joystick to fly it in real time, like a video game. Instead, they need to send commands to the helicopter in advance, and the little flying robot will follow through. Autonomous systems will allow the helicopter to look at the ground, analyze the terrain to look how fast it’s moving, and land on its own.
10. It could pave the way for future missions.
A future Mars helicopter could scout points of interest, help scientists and engineers select new locations and plan driving routes for a rover. Larger standalone helicopters could carry science payloads to investigate multiple sites at Mars. Future helicopters could also be used to fly to places on Mars that rovers cannot reach, such as cliffs or walls of craters. They could even assist with human exploration one day. Says Balaram: “Someday, if we send astronauts, these could be the eyes of the astronauts across Mars.”
Read the full version of this week’s ‘10 Things to Know’ article on the web HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.


It’s National Donut Day and these galactic donuts by H.Rebel are truly the only way for a startorialist to properly celebrate!
H.Rebel is located in Tehran and blogs about her love of food, photography, and food photography here. What’s more is if you look closely at the top photo, you’ll notice she’s also a fan of one of our favs: Eclectic Eccentricity! Startorial worlds colliding!
If you can’t find the energy to make some stellar donuts yourself, those of you in the Seattle area can grab a snack at the fabulously named, Galaxy Donuts (which doesn’t offer space donuts, BUT TOTALLY SHOULD).
- Summer
What are the Universe’s Most Powerful Particle Accelerators?
Every second, every square meter of Earth’s atmosphere is pelted by thousands of high-energy particles traveling at nearly the speed of light. These zippy little assailants are called cosmic rays, and they’ve been puzzling scientists since they were first discovered in the early 1900s. One of the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope’s top priority missions has been to figure out where they come from.

“Cosmic ray” is a bit of a misnomer. Makes you think they’re light, right? But they aren’t light at all! They’re particles that mostly come from outside our solar system — which means they’re some of the only interstellar matter we can study — although the Sun also produces some. Cosmic rays hit our atmosphere and break down into secondary cosmic rays, most of which disperse quickly in the atmosphere, although a few do make it to Earth’s surface.
Cosmic rays aren’t dangerous to those of us who spend our lives within Earth’s atmosphere. But if you spend a lot of time in orbit or are thinking about traveling to Mars, you need to plan how to protect yourself from the radiation caused by cosmic rays.

Cosmic rays are subatomic particles — smaller particles that make up atoms. Most of them (99%) are nuclei of atoms like hydrogen and helium stripped of their electrons. The other 1% are lone electrons. When cosmic rays run into molecules in our atmosphere, they produce secondary cosmic rays, which include even lighter subatomic particles.

Most cosmic rays reach the same amount of energy a small particle accelerator could produce. But some zoom through the cosmos at energies 40 million times higher than particles created by the world’s most powerful man-made accelerator, the Large Hadron Collider. (Lightning is also a pretty good particle accelerator).

So where do cosmic rays come from? We should just be able to track them back to their source, right? Not exactly. Any time they run into a strong magnetic field on their way to Earth, they get deflected and bounce around like a game of cosmic pinball. So there’s no straight line to follow back to the source. Most of the cosmic rays from a single source don’t even make it to Earth for us to measure. They shoot off in a different direction while they’re pin balling.

Photo courtesy of Argonne National Laboratory
In 1949 Enrico Fermi — an Italian-American physicist, pioneer of high-energy physics and Fermi satellite namesake — suggested that cosmic rays might accelerate to their incredible speeds by ricocheting around inside the magnetic fields of interstellar gas clouds. And in 2013, the Fermi satellite showed that the expanding clouds of dust and gas produced by supernovas are a source of cosmic rays.

When a star explodes in a supernova, it produces a shock wave and rapidly expanding debris. Particles trapped by the supernova remnant magnetic field bounce around wildly.

Every now and then, they cross the shock wave and their energy ratchets up another notch. Eventually they become energetic enough to break free of the magnetic field and zip across space at nearly the speed of light — some of the fastest-traveling matter in the universe.

How can we track them back to supernovas when they don’t travel in a straight line, you ask? Very good question! We use something that does travel in a straight line — gamma rays (actual rays of light this time, on the more energetic end of the electromagnetic spectrum).
When the particles get across the shock wave, they interact with non-cosmic-ray particles in clouds of interstellar gas. Cosmic ray electrons produce gamma rays when they pass close to an atomic nucleus. Cosmic ray protons, on the other hand, produce gamma rays when they run into normal protons and produce another particle called a pion (Just hold on! We’re almost there!) which breaks down into two gamma rays.

The proton- and electron-produced gamma rays are slightly different. Fermi data taken over four years showed that most of the gamma rays coming from some supernova remnants have the energy signatures of cosmic ray protons knocking into normal protons. That means supernova remnants really are powerful particle accelerators, creating a lot of the cosmic rays that we see!
There are still other cosmic ray sources on the table — like active galactic nuclei — and Fermi continues to look for them. Learn more about what Fermi’s discovered over the last 10 years and how we’re celebrating its accomplishments.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
10 Things: Journey to the Center of Mars
May the fifth be with you because history is about to be made: As early as May 5, 2018, we’re set to launch Mars InSight, the very first mission to study the deep interior of Mars. We’ve been roaming the surface of Mars for a while now, but when InSight lands on Nov. 26, 2018, we’re going in for a deeper look. Below, 10 things to know as we head to the heart of Mars.

Coverage of prelaunch and launch activities begins Thursday, May 3, on NASA Television and our homepage.
1. What’s in a name?

“Insight” is to see the inner nature of something, and the InSight lander—a.k.a. Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport—will do just that. InSight will take the “vital signs” of Mars: its pulse (seismology), temperature (heat flow) and reflexes (radio science). It will be the first thorough check-up since the planet formed 4.5 billion years ago.
2. Marsquakes.
You read that right: earthquakes, except on Mars. Scientists have seen a lot of evidence suggesting Mars has quakes, and InSight will try to detect marsquakes for the first time. By studying how seismic waves pass through the different layers of the planet (the crust, mantle and core), scientists can deduce the depths of these layers and what they’re made of. In this way, seismology is like taking an X-ray of the interior of Mars.
Want to know more? Check out this one-minute video.
3. More than Mars.

InSight is a Mars mission, but it’s also so much more than that. By studying the deep interior of Mars, we hope to learn how other rocky planets form. Earth and Mars were molded from the same primordial stuff more than 4.5 billion years ago, but then became quite different. Why didn’t they share the same fate? When it comes to rocky planets, we’ve only studied one in great detail: Earth. By comparing Earth’s interior to that of Mars, InSight’s team hopes to better understand our solar system. What they learn might even aid the search for Earth-like planets outside our solar system, narrowing down which ones might be able to support life.
4. Robot testing.
InSight looks a bit like an oversized crane game: When it lands on Mars this November, its robotic arm will be used to grasp and move objects on another planet for the first time. And like any crane game, practice makes it easier to capture the prize.
Want to see what a Mars robot test lab is like? Take a 360 tour.
5. The gang’s all here.

InSight will be traveling with a number of instruments, from cameras and antennas to the heat flow probe. Get up close and personal with each one in our instrument profiles.
6. Trifecta.

InSight has three major parts that make up the spacecraft: Cruise Stage; Entry, Descent, and Landing System; and the Lander. Find out what each one does here.
7. Solar wings.
Mars has weak sunlight because of its long distance from the Sun and a dusty, thin atmosphere. So InSight’s fan-like solar panels were specially designed to power InSight in this environment for at least one Martian year, or two Earth years.
8. Clues in the crust.

Our scientists have found evidence that Mars’ crust is not as dense as previously thought, a clue that could help researchers better understand the Red Planet’s interior structure and evolution. “The crust is the end-result of everything that happened during a planet’s history, so a lower density could have important implications about Mars’ formation and evolution,” said Sander Goossens of our Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
9. Passengers.

InSight won’t be flying solo—it will have two microchips on board inscribed with more than 2.4 million names submitted by the public. “It’s a fun way for the public to feel personally invested in the mission,” said Bruce Banerdt of our Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the mission’s principal investigator. “We’re happy to have them along for the ride.”
10. Tiny CubeSats, huge firsts.

The rocket that will loft InSight beyond Earth will also launch a separate NASA technology experiment: two mini-spacecraft called Mars Cube One, or MarCO. These suitcase-sized CubeSats will fly on their own path to Mars behindInSight. Their goal is to test new miniaturized deep space communication equipment and, if the MarCOs make it to Mars, may relay back InSight data as it enters the Martian atmosphere and lands. This will be a first test of miniaturized CubeSat technology at another planet, which researchers hope can offer new capabilities to future missions.
Check out the full version of ‘Solar System: 10 Thing to Know This Week’ HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Earth: Your Home, Our Mission
We pioneer and support an amazing range of advanced technologies and tools to help us better understand our home planet, the solar system and far beyond.
Here are 5 ways our tech improves life here on Earth…
1. Eyes in the Sky Spot Fires on the Ground

Our Earth observing satellites enable conservation groups to spot and monitor fires across vast rainforests, helping them protect our planet on Earth Day and every day.
2. Helping Tractors Drive Themselves

There has been a lot of talk about self-driving cars, but farmers have already been making good use of self-driving tractors for more than a decade - due in part to a partnership between John Deere and our Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Growing food sustainably requires smart technology - our GPS correction algorithms help self-driving tractors steer with precision, cutting down on water and fertilizer waste.
3. Turning Smartphones into Satellites

On Earth Day (and every day), we get nonstop “Earth selfies” thanks to Planet Labs’ small satellites, inspired by smartphones and created by a team at our Ames Research Center. The high res imagery helps conservation efforts worldwide.
4. Early Flood Warnings

Monsoons, perhaps the least understood and most erratic weather pattern in the United States, bring rain vital to agriculture and ecosystems, but also threaten lives and property. Severe flash-flooding is common. Roads are washed out. Miles away from the cloudburst, dry gulches become raging torrents in seconds. The storms are often accompanied by driving winds, hail and barrages of lightning.
We are working to get better forecasting information to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Our satellites can track moisture in the air - helping forecasters provide an early warning of flash floods from monsoons.
5. Watching the World’s Water

Around the world, agriculture is by far the biggest user of freshwater. Thanks in part to infrared imagery from Landsat, operated by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), we can now map, in real time, how much water a field is using, helping conserve that precious resource.
We use the vantage point of space to understand and explore our home planet, improve lives and safeguard our future. Our observations of Earth’s complex natural environment are critical to understanding how our planet’s natural resources and climate are changing now and could change in the future.
Join the celebration online by using #NASA4Earth.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Earth from Afar
“It suddenly struck me that that tiny pea, pretty and blue, was the Earth. I put up my thumb and shut one eye, and my thumb blotted out the planet Earth. I didn’t feel like a giant. I felt very, very small.” - Neil Armstrong, Apollo 11

This week we’re celebrating Earth Day 2018 with some of our favorite images of Earth from afar…
At 7.2 million Miles…and 4 Billion Miles

Voyager famously captured two unique views of our homeworld from afar. One image, taken in 1977 from a distance of 7.3 million miles (11.7 million kilometers) (above), showed the full Earth and full Moon in a single frame for the first time in history. The second (below), taken in 1990 as part of a “family portrait of our solar system from 4 billion miles (6.4 billion kilometers), shows Earth as a tiny blue speck in a ray of sunlight.” This is the famous “Pale Blue Dot” image immortalized by Carl Sagan.

“This was our willingness to see the Earth as a one-pixel object in a far greater cosmos,” Sagan’s widow, Ann Druyan said of the image. “It’s that humility that science gives us. That weans us from our childhood need to be the center of things. And Voyager gave us that image of the Earth that is so heart tugging because you can’t look at that image and not think of how fragile, how fragile our world is. How much we have in common with everyone with whom we share it; our relationship, our relatedness, to everyone on this tiny pixel.“
A Bright Flashlight in a Dark Sea of Stars

Our Kepler mission captured Earth’s image as it slipped past at a distance of 94 million miles (151 million kilometers). The reflection was so extraordinarily bright that it created a saber-like saturation bleed across the instrument’s sensors, obscuring the neighboring Moon.
Hello and Goodbye

This beautiful shot of Earth as a dot beneath Saturn’s rings was taken in 2013 as thousands of humans on Earth waved at the exact moment the spacecraft pointed its cameras at our home world. Then, in 2017, Cassini caught this final view of Earth between Saturn’s rings as the spacecraft spiraled in for its Grand Finale at Saturn.
‘Simply Stunning’

”The image is simply stunning. The image of the Earth evokes the famous ‘Blue Marble’ image taken by astronaut Harrison Schmitt during Apollo 17…which also showed Africa prominently in the picture.“ -Noah Petro, Deputy Project Scientist for our Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter mission.
Goodbye—for now—at 19,000 mph

As part of an engineering test, our OSIRIS-REx spacecraft captured this image of Earth and the Moon in January 2018 from a distance of 39.5 million miles (63.6 million kilometers). When the camera acquired the image, the spacecraft was moving away from our home planet at a speed of 19,000 miles per hour (8.5 kilometers per second). Earth is the largest, brightest spot in the center of the image, with the smaller, dimmer Moon appearing to the right. Several constellations are also visible in the surrounding space.
The View from Mars

A human observer with normal vision, standing on Mars, could easily see Earth and the Moon as two distinct, bright "evening stars.”
Moon Photobomb

“This image from the Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR) satellite captured a unique view of the Moon as it moved in front of the sunlit side of Earth in 2015. It provides a view of the far side of the Moon, which is never directly visible to us here on Earth. “I found this perspective profoundly moving and only through our satellite views could this have been shared.” - Michael Freilich, Director of our Earth Science Division.
Eight Days Out

Eight days after its final encounter with Earth—the second of two gravitational assists from Earth that helped boost the spacecraft to Jupiter—the Galileo spacecraft looked back and captured this remarkable view of our planet and its Moon. The image was taken from a distance of about 3.9 million miles (6.2 million kilometers).
A Slice of Life

Earth from about 393,000 miles (633,000 kilometers) away, as seen by the European Space Agency’s comet-bound Rosetta spacecraft during its third and final swingby of our home planet in 2009.
So Long Earth

The Mercury-bound MESSENGER spacecraft captured several stunning images of Earth during a gravity assist swingby of our home planet on Aug. 2, 2005.
Earth Science: Taking a Closer Look

Our home planet is a beautiful, dynamic place. Our view from Earth orbit sees a planet at change. Check out more images of our beautiful Earth here.
Join Our Earth Day Celebration!
We pioneer and supports an amazing range of advanced technologies and tools to help scientists and environmental specialists better understand and protect our home planet - from space lasers to virtual reality, small satellites and smartphone apps.
To celebrate Earth Day 2018, April 22, we are highlighting many of these innovative technologies and the amazing applications behind them.
Learn more about our Earth Day plans HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How does a microgravity garden grow when there’s no up or down? An advanced chamber, about the size of a mini-fridge, is giving us a clearer perspective of plant growth habits. Without gravity and the addition of a wide variety of light and humidity settings, the plants cultivated on the International Space Station provide a world of opportunity to study space-based agricultural cycles.
Learn more about our space garden HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Totally.

“advantages of being a woman artist” by guerrilla girls (1989)
Inspirational!
Solar System 10 Things to Know This Week: Humans of NASA
Meet some of the amazing humans behind our exploring machines.
1—Small Town to Small Satellites

“I grew up in a small town where working at NASA was unheard of. I worked hard, persevered, and eventually made it to where I am despite many obstacles along the way. Through that process, never forget to enjoy what you are doing. It is my passion for space exploration that has helped me keep motivated and that brings me happiness every day that I come to work.”
—Farah Alibay, Engineer
2—Scientist. Mountain Unicyclist

“I do a rather unusual sport for fun—mountain unicycling. I love it because it’s incredibly challenging, requiring strength, stamina and focus. I also enjoy surfing, caving, flying and teaching a space camp in South Korea each summer.”
—Morgan Cable, Research Scientist
3—"Eat. Breathe. Do Science. Sleep later.“

“I do SCIENCE! No, seriously, I travel and explore for fun. It’s a fascinating world and I can’t get enough of it. But I’m always doing "science” of some kind no matter where I am. I love it —— can’t escape it and wouldn’t want to. Eat. Breathe. Do Science. Sleep later.”
—Derek Pitts, Solar System Ambassador
4—In the Room Where It Happened

“It was the summer of 2013, when I was the media rep for the Voyager mission. I was with Ed Stone, the mission’s project scientist, when he came to the conclusion that Voyager 1 had crossed the threshold into interstellar space. For the first time, a human—made object flew beyond the plasma bubble our sun blows around itself. Voyager 1 is now bathed in the remnants of the explosions of other stars. I really appreciated seeing the scientific process—and Ed’s mind—at work.”
—Jia-Rui Cook, Supervisor of News Events and Projects at JPL
5—All About the Math. And Determination.

“From an academic point of view, it’s all about doing well in math and science. However, there is absolutely no substitute for being determined. Being determined to be successful is at least half the game.”
— James Green, Director of NASA’s Planetary Science Division
6—Problem Solver

“Opportunity [rover] was designed to live for 90 days in the harsh Martian environment but she is still exploring now 11 years later! Because of her age, software and hardware components are degrading on the vehicle and more recently, the flash memory. I had the incredible opportunity to lead the team to figure out how to solve these flash problems and get Opportunity back into an operational state.”
—Bekah Sosland Siegfriedt, Engineer
7—Never Give Up

“When you encounter difficulties or failures, do not take no for an answer. If you truly want to accomplish something and are passionate about it, you need to believe in yourself, put your mind to it, and you can accomplish anything! I failed A LOT, but I NEVER GAVE UP. It took three years and over 150 applications to NASA before I received my first internship”
—Kevin DeBruin, Systems Engineer
8—More Than Mohawk Guy

“The great thing about being at NASA is that there are jobs for all types —— whether it’s engineering, science, finance, communication, law, and so forth. All of them are necessary and all of them involve working on some of the coolest things humans can do. So pick the area you love, but also know that you can still be a part of exploring the universe.”
—Bobak Ferdowsi, Systems Engineer
9—The Power of One

“When my older sister claimed she would one day be an astronaut, on the heels of Sally Ride’s launch into space, I made the same claim. Though, it was more because I dreamed to be just like my sister! In turned out that she outgrew the crazy dream, and my desire only got stronger.”
—Mamta Patel Nagaraja, Science Communications
10—Dedication and Choices

“Body-building is a favorite pasttime: it’s a great stress reliever and a hobby that I can take with me when I travel for work or for pleasure. It’s also a great expression of responsibility and ownership: What I’ve accomplished is due entirely to my dedication and choices, and it belongs to no one but me.”
—Troy Hudson, Instrument System Engineer
Check out the full version of Ten Things to Know HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com


The next Warriors upcoming books.
Love Warriors!









Super Edition and Field Guide cover art.
(This is the end of my collection of the original cover art. Hopefully at some point, HarperCollins releases the rest of it, because it’s so good.)
Love foxes!

What’s Up - February 2018
What’s Up For February?

This month, in honor of Valentine’s Day, we’ll focus on celestial star pairs and constellation couples.

Let’s look at some celestial pairs!

The constellations Perseus and Andromeda are easy to see high overhead this month.

According to lore, the warrior Perseus spotted a beautiful woman–Andromeda–chained to a seaside rock. After battling a sea serpent, he rescued her.

As a reward, her parents Cepheus and Cassiopeia allowed Perseus to marry Andromeda.

The great hunter Orion fell in love with seven sisters, the Pleiades, and pursued them for a long time. Eventually Zeus turned both Orion and the Pleiades into stars.

Orion is easy to find. Draw an imaginary line through his belt stars to the Pleiades, and watch him chase them across the sky forever.

A pair of star clusters is visible on February nights. The Perseus Double Cluster is high in the sky near Andromeda’s parents Cepheus and Cassiopeia.

Through binoculars you can see dozens of stars in each cluster. Actually, there are more than 300 blue-white supergiant stars in each of the clusters.

There are some colorful star pairs, some visible just by looking up and some requiring a telescope. Gemini’s twins, the brothers Pollux and Castor, are easy to see without aid.

Orion’s westernmost, or right, knee, Rigel, has a faint companion. The companion, Rigel B, is 500 times fainter than the super-giant Rigel and is visible only with a telescope.

Orion’s westernmost belt star, Mintaka, has a pretty companion. You’ll need a telescope.

Finally, the moon pairs up with the Pleiades on the 22nd and with Pollux and Castor on the 26th.
Watch the full What’s Up for February Video:
There are so many sights to see in the sky. To stay informed, subscribe to our What’s Up video series on Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.





















